Treating river water for domestic use and industrial production is a necessary need, however, to produce satisfactory post-treatment quality, it is necessary to clearly understand the properties and master treatment techniques.
Facility for selecting locations to collect river water
- Upstream compared to residential and industrial areas
- River banks and river beds are stable, with no (or little) landslides and sedimentation; Unaffected by waves and tides
- Obtain water of good quality and sufficient flow for current and future development planning; Convenient for protecting water source hygiene
- Must be combined with other projects in the industrial system to form a reasonable and economic whole
- Near the electricity supply
River water treatment technology
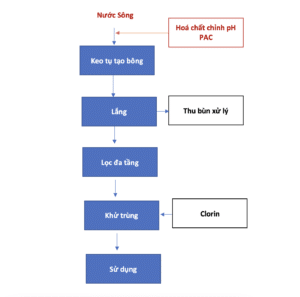
Technological diagram of river water treatment system
River water should be taken from locations that avoid wastewater sources. If possible, water should be chosen from the main branch instead of the child branch.
Nam Viet Construction of river water sedimentation flocculation tank cluster in Ben Tre

Check the water pump for leaks before installing the device
Flocculation
- Commonly used coagulant chemical is PAC (Poly Aluminum Chloride) dosage 15-30 g/m3
- Mix into a 10-20% solution.
- If the flocculation is not good, you can add chemicals to raise the pH to 6.5-8.5 to increase flocculation efficiency.
- Coagulation tanks can be built from concrete or made of steel equipment.

Flocculation chemical pump assembly
Settle
- River water after adding coagulant chemicals is passed through the sedimentation tank to settle the sludge
- Clean water is passed through the filter.
- A bottom discharge valve must be designed to discharge sludge.
- Beveled the corner to create a funnel top for easy sludge discharge.
- Sedimentation tanks can also be constructed of concrete or machined from steel.

Nam Viet installs sedimentation equipment for the river water treatment tank complex

Completion of river water sedimentation tank
Filter
- Pressure filtration equipment is intended to remove suspended sediments that are small in size and cannot settle.
- Depending on the purpose of use, coarse filtration (coal, sand and gravel) can be used or a combination of coarse filtration and fine filtration (compressed core).
- Periodically clean the filter to avoid clogging.

Cluster of sand filter, activated carbon, fine filter equipment
Disinfect river water after treatment
River water, after going through the filtration stages, basically looks clear and clean to the senses. However, disinfection is needed to kill disease-causing bacteria such as Ecoli and Coliform
There are many options for water disinfection: ozone, Javen, UV, Chlorine… However, the most popular option is Chlorin because of its effectiveness and cost savings.
Standards for water use per person/day
- Is the average amount of water consumed by 1 person in 1 day and night or for 1 unit of product (l/person.day) or (m3/ton of product.day)
- Is the basic parameter to determine the scale/capacity of industrial system
- Types of water use standards: domestic, industrial, commercial, service, watering plants, washing roads, firefighting, leaks, losses…
- General water use standards per capita (TCXDVN 33:2006)
| Subjects using water | Water supply standards per capita l/person.day (average day of the year) |
| Big city, tourist city, resort, large industrial park. | 300 – 400 |
| Cities, small and medium towns, small industrial parks | 200 – 270 |
| Town, industrial – agricultural, industrial – fishery center, rural residential area | 80 – 150 |
| Countryside
| 40 – 60 |
Standards for domestic water use
Depends on 2 main factors:
- Level of sanitary equipment inside the building
- Climatic conditions and customs of each locality
When there is data on population density and classification according to level of amenities
Different types of urban areas will have different standards for domestic water use
| STT
| Comfort level of the house | TC Water supply (liter/person.day) |
| 1. | The house does not have toilet facilities and uses public water taps | 40 – 60 |
| 2. | The house only has a faucet, no sanitary equipment | 80 – 100 |
| 3. | The house has an internal drainage system, sanitary equipment but no shower | 120-150 |
| 4. | The house has sanitary equipment and a shower | 150-200 |
| 5. | As above and with hot tub | 200-300 |
River water characteristics
- It is the main water source to supply water for daily life and industry today
- Abundant water reserves, changing seasonally
- Directly affected by domestic and industrial wastewater
- Water quality depends on soil and vegetation cover
- However, rivers have the ability to clean themselves
- High turbidity, lots of silt and algae.
- Low Dissolved Solids (TDS).
- Low total hardness
- Chloride (Cl-) is low (except in saline areas).
Some physicochemical properties of river water
Temperature:
Is a factor related to the survival and development of aquatic organisms, and is also a factor that affects the rate of biological decomposition of organic pollutants in water, affecting dissolved oxygen concentration. . Thereby affecting the self-cleaning ability of natural water sources, changes in temperature affect water quality in many ways. Temperature is the factor that determines which species of organisms predominate in the aquatic environment. (In Vietnam, the water temperature ranges from 13-34oC “according to Trinh Xuan Lai”) According to depth, the temperature is divided into 3 clear layers: Surface layer, transition layer and bottom layer.
In the surface layer: water has high temperature so density is low. Due to the influence of wind, the water in the surface layer is strongly disturbed, causing the temperature to be relatively uniform, the dissolved oxygen concentration is high, and light reception is good, so photosynthesis takes place strongly. This layer is very favorable for biological decomposition.
Transition layer: has a clear decrease in temperature with depth
At the bottom layer, the water is not stirred and is separated from the surface layer by the transition layer, so the dissolved oxygen concentration is low and sunlight does not penetrate. In this layer, the organic decomposition process takes place under anaerobic conditions, the decomposition products are odorous and toxic H2S, NH3
Color
The color of water is due to substances created during the decomposition of organic debris such as leaves, wood… or inorganic compounds containing Fe (III) when present in the water sample. Natural color-causing components in water are in the form of colloidal particles with negative charges, so they can be removed by coagulation with salts of trivalent metal ions such as Fe and Al. The color of water is caused by suspended substances that are removed by filtration. The color of water caused by dissolved substances is removed by combined physical and chemical methods
Water contaminated by domestic and industrial wastewater is often dark green or black.
Color is measured in PtCo (Platin-cobalt) units. Natural water has a color value of less than 200 PtCo
Based on water color to decide the level of treatment and choose treatment methods and chemicals used in treatment (according to Trinh Xuan Lai, natural water usually has a color lower than 200 degrees (ptCo)).
Turbidity
The turbidity of water is due to the presence of many types of colloidal or coarsely dispersed suspended substances in the water that are washed from the basin surface into the water body. Turbidity is determined by the ability of light to spread through water. It reflects the degree to which inorganic and organic suspended matter prevent light from penetrating water. Through turbidity, water contamination can be assessed… The unit of measurement for turbidity is NTU, surface water has turbidity of 20-100 NTU. Flood season reaches 500 NTU. Drinking water supply is less than 5 NTU
Taste
Polluted water has an odor due to chemical compounds, mainly organic compounds or products from material decomposition. Water is heavily polluted by organic substances and has a very unpleasant odor due to toxic gases such as SO2, H2S products from anaerobic digestion.
Electrical conductivity
Electrical conductivity increases with the content of dissolved minerals in the water and fluctuates with temperature. Used to evaluate the total amount of dissolved minerals in water. pure water in 20oc To be 4,2 µs/m
Radioactivity
Radioactivity is caused by the decomposition of radioactive components in water. Determined through the sum of alpha and beta radioactivity.
Total solids
The total number of solids is all the substances present in the water, determined by drying the water sample at a temperature of 103 – 105 degrees. After the water has evaporated, the remainder is solid. Solids present in water include dissolved and suspended solids, the most important of which are suspended solids
Chất rắn lơ lửng
The amount of suspended solids is a parameter to evaluate wastewater intensity and efficiency of treatment equipment. Determine the method of filtering the water sample using a Gut cup, then measure the mass of solids in the filter membrane of the cup (mg/l).
Nam Viet Environmental Engineering Joint Stock Company receives river water treatment for production and daily life, installs industrial RO systems with optimal technology, high quality, reasonable price, easy to operate and maintain. maintain. Please contact us for a free consultation.
Hotline 0932562177



Bài viết liên quan
Drinking water treatment for pigs and issues to note
Drinking water for pigs in particular and water treatment in livestock farming in general is...
Pure RO bottled water filtration system
What is a bottled water filtration system? The bottled water filtration system is essentially an...
Commonly applied water disinfection methods
Water disinfection is a mandatory step in the drinking and drinking process. Natural water contains...